- Home
- Products
- Wet Scrubbers
Venturi Scrubber
Venturi Wet Dust Scrubbers
Ideally suited to industrial processes that need to capture sub-micron particles with minimal downtime and maintenance.
MikroPul’s flexible designs are well suited to solving problems across multiple industries. These include mining, chemicals, food, pulp & paper, explosive dust and metals applications, such as HCl and particulate removal in Aluminum refining. MikroPul venturi scrubbers are designed for long working life with minimal maintenance. Our experienced engineers deliver superior yet simple venturi scrubber designs in appropriate materials, with optimized features to suit your specific application.
Nederman MikroPul venturi scrubbers are valuable in processes needing high particulate removal efficiency, typically greater than 99.9% for sub-micron particles. They excel in high inlet gas temperatures, high dust/particle loading and high percentage of solids in the liquid recirculation loop.
Multi-Venturi Scrubbers are also available with special features to address applications where the user desires high performance at low pressure drops, adjustability of the venturi rod deck or compact, low profile design to suit available space. Additionally, these designs are self-draining and do not require water level control.
What is a Venturi Scrubber and how does it work?

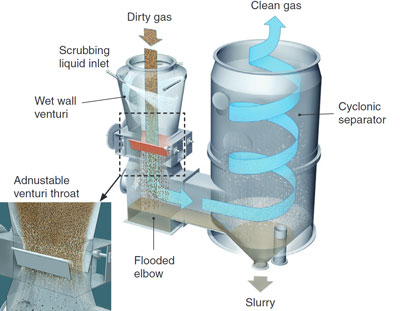
Dirty gas enters the venturi scrubber
The dirty gas instantly make contact with the tangentially introduced scrubbing liquid
The dirty gas swirls down the venturi’s converging walls
At the adjustable venturi throat, the gas and liquid streams collide and the liquid breaks down into droplet, which trap dust particles
The gas/liquid mixture passes through the flooded elbow and enters the entrainment separator though a tangential inlet
Centrifugal action removes the heavy wetted particles from the gas stream
The dust/liquid mixture is discharged from the separator bottom drain
Cleaned gas leaves through the top of the separator
- Dirty gas enters the venturi scrubber
- The dirty gas instantly make contact with the tangentially introduced scrubbing liquid
- The dirty gas swirls down the venturi’s converging walls
- At the adjustable venturi throat, the gas and liquid streams collide and the liquid breaks down into droplet, which trap dust particles
- The gas/liquid mixture passes through the flooded elbow and enters the entrainment separator though a tangential inlet
- Centrifugal action removes the heavy wetted particles from the gas stream
- The dust/liquid mixture is discharged from the separator bottom drain
- Cleaned gas leaves through the top of the separator

99.9%+ effciency for sub-micron particles

Ideal for handling high temperature gas

Minimal maintenance with long operation life

Flexible design to meet your application needs
Typical applications where venturi scrubbers are used

Mining

Chemicals

Food

Mettalurgy
The basic designs are:
Venturi Wet Scrubber
The design of the MikroPul Venturi Scrubber consists of a “wet approach” venturi followed by a liquid entrainment separator. Dust-laden gases enter the venturi and instantly make contact with the tangentially introduced scrubbing liquid swirling down the venturi’s converging walls.
At the adjustable venturi throat, the gas and liquid streams collide and the liquid breaks down into droplets which trap dust particles. This gas/liquid mixture passes through a flooded elbow and then enters the entrainment separator through a tangential inlet. A cyclonic separator then removes the heavy wetted particles from the gas stream. Alternatively, when very large diameter separation is required, the liquid is separated by passing the stream through a chevron-type mist eliminator baffle.
The dust/liquid mixture is discharged from the separator bottom drain and the cleaned gas leaves through the top of the separator.
This design has minimum maintenance since it uses open pipe liquid inlets with no spray nozzles.
What scrubbing liquid is used in a chemical scrubber?
Scrubbing liquid reagent selection depends on what chemical is being treated in the scrubber. Typically, scrubbing liquids are an acid, a base or sodium hypochlorite. Common examples of such include caustic, sulfuric acid and phosphoric acid.
Venturi Scrubbers have several advantages compared to filters and other dust collection equipment; not only is the overall size of the equipment often small, but they can handle particle-laden gas streams that are high temperatures or contain moisture.
Other advantages relate to ease of maintenance and choice of construction options; aside from having a system fan and recirculation pump, venturi scrubbers are solid state and have continuous blow-down of the scrubbing liquid & freshwater makeup, which decreases the frequency of cleaning. An additional Clean-In-Place (CIP) manifold system - a series of internal nozzles complete with piping, valving, and chemical injection ports - can integrate to provide further ease of maintenance.
Advantages of Venturi Scrubbers
Multi-Stage Venturi Wet Scrubber
The multi-stage venturi wet scrubber is for applications where one stage of wet scrubbing is not enough to completely remove the particular dirty gas particles from the air flow.
Multi-Venturi Wet Scrubber
This scrubber makes use of a venturi-rod deck consisting of a series of rods arranged to create a venturi effect between each rod. It offers higher efficiencies at lower pressure drops and liquid to gas ratios than conventional venturi scrubbers.
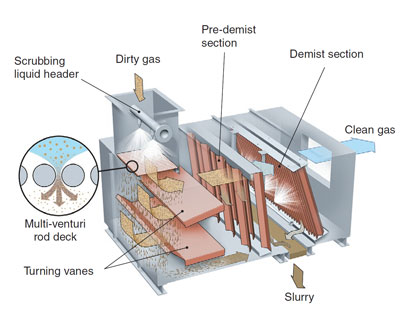
Dust laden gases are directed through the venturi-rod deck where atomized scrub water is introduced co-currently with the gas stream. The scrub water is sprayed through a series of low pressure, large orifice nozzles, distributing it evenly across the deck. The gas rapidly accelerates as it passes through the venturi-rods. This action creates smaller droplets, causing encapsulation of the particles and increasing the collection efficiency of submicron particles.
As the gases exit the venturi-rod area, velocity slows causing the larger particle-laden droplets to fall out of the stream. The scrubbed gasses are then directed toward a two-stage demisting zone by distribution baffles or turning vanes. Primary demisting and gas distribution occurs in the pre-demist area, which removes 90% of the water. The remaining free water droplets are removed by impingement on the final stage demist vanes. The scrub water collected prior to the demist section flows down the scrubber floor to the drain trough. Dewatered scrubbed gases are exhausted via the scrubber outlet.
This design utilizes rod-deck design that is easy to maintain.
Contact us to create your custom solution
Call us at: 704-399-7441 or fill out the form below.